This article delves into the realm of arthritis joint pain treatment, offering insights into various therapeutic strategies aimed at alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life. Arthritis encompasses a range of inflammatory joint conditions, characterized by pain, stiffness, and swelling. Treatment approaches vary from medication and physical therapy to innovative interventions, each tailored to disease severity and patient needs.
Arthritis is a term used to describe a multitude of joint-related conditions marked by inflammation, pain, and stiffness. There are over 100 types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout. Each type has its unique set of causes and treatment methodologies, impacting millions globally. Osteoarthritis, the most common form, occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones wears down over time, leading to pain and reduced mobility. Conversely, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing inflammation and possibly joint deformity. Gout is characterized by sudden and severe attacks of pain, redness, and swelling in joints, usually due to excess uric acid in the bloodstream. The complexity of this condition necessitates tailored approaches for effective management, making understanding its intricacies essential for optimized care.
When it comes to arthritis joint pain treatment, there are several strategies, each designed to meet specific needs and disease profiles. A multidisciplinary approach that incorporates medical treatments, physical rehabilitation, and patient education often yields the best outcomes.
Medicines are crucial in managing arthritis symptoms and slowing disease progression. Common medications include Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, and analgesics. NSAIDs help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain, while DMARDs and biologics aim to slow the disease process, particularly in autoimmune forms like rheumatoid arthritis. For example, NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen are often used as first-line treatments, while DMARDs such as methotrexate and biologics like adalimumab are used in more advanced cases. In certain situations, corticosteroids may also be prescribed to provide rapid relief from inflammation.
Physical therapy is a key component of arthritis management, focusing on maintaining joint function, improving range of motion, and strengthening muscles around the joints. Tailored exercise programs designed by physiotherapists can significantly reduce pain and increase joint flexibility, providing good benefits in managing arthritis symptoms. Activities such as swimming, walking, and cycling are generally recommended as they place minimal stress on the joints while promoting strength and mobility. In collaboration with physical therapists, patients can identify exercises that suit their specific condition and capabilities. Furthermore, techniques like aquatic therapy may provide a supportive environment to alleviate pressure on the joints while enhancing overall fitness.
For severe cases of arthritis, surgical options such as joint replacement or arthroscopy may be considered. These procedures are generally recommended when conservative treatments fail to provide relief and when joint damage significantly impairs daily activities. Joint replacement surgery involves replacing a damaged joint with an artificial one, commonly performed in hips and knees. Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure where a small camera is inserted into the joint, allowing surgeons to diagnose and possibly repair internal issues such as torn menisci or loose cartilage. Post-operative rehabilitation is essential for maximizing outcomes and restoring function.
In recent years, innovative treatments have emerged, offering new hope for arthritis sufferers. As research progresses, several advanced therapies show potential in managing arthritis more effectively.
Stem cell therapy is a cutting-edge treatment that aims to regenerate damaged joint tissues, potentially altering the course of the disease. Although still under investigation, early results indicate promising outcomes, especially for osteoarthritis. Researchers are exploring different types of stem cells, including those derived from bone marrow and adipose (fat) tissue, to determine their effectiveness in rebuilding cartilage and reducing inflammation. While practical applications are still being refined, the future of regenerative medicine offers exciting possibilities for long-term healing and restoration of joint function.
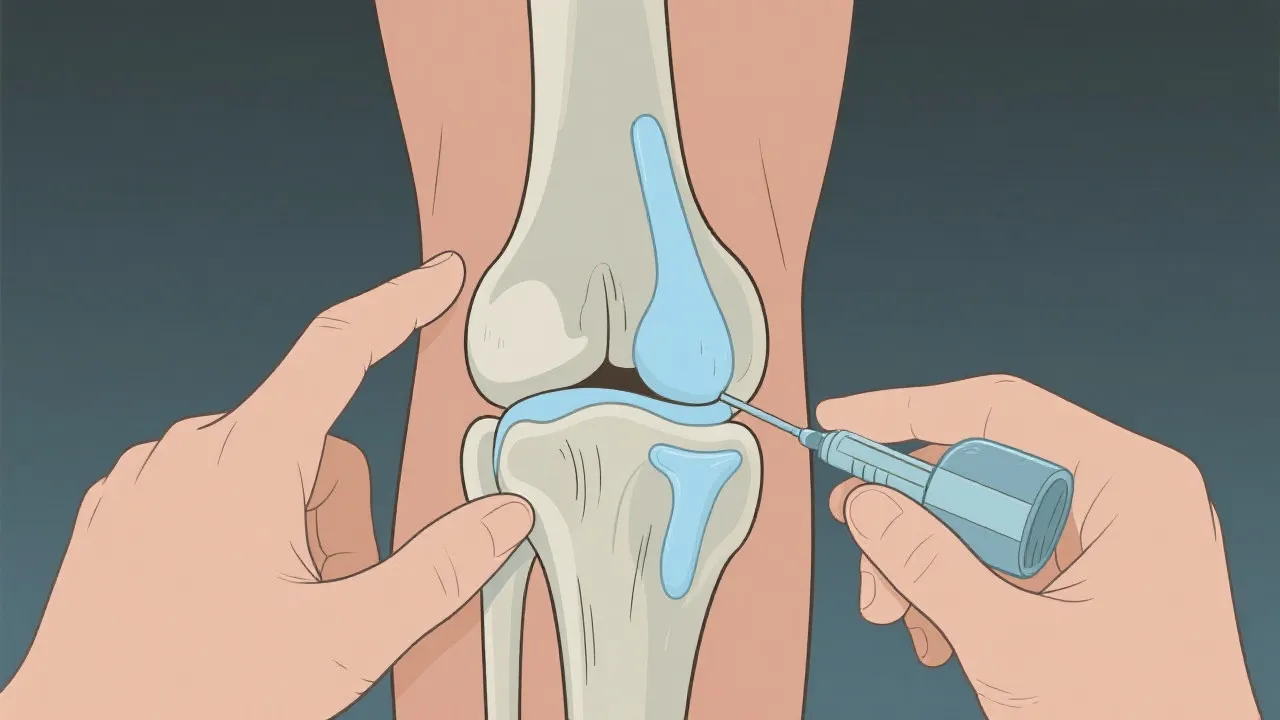
PRP therapy involves using a concentration of a patient’s own platelets to accelerate healing of injured tendons, ligaments, and joints. This innovative treatment has gained attention for its non-surgical approach and for its potential to alleviate pain while promoting tissue healing. The procedure involves drawing a small amount of blood from the patient, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting this platelet-rich plasma into the affected joint. Studies suggest this method may reduce inflammation and stimulate the body’s natural healing processes, providing an alternative for patients seeking non-surgical options. Although further research is needed to establish long-term benefits, initial findings have led to increased interest in PRP therapy as a viable option for arthritis treatment.
In addition to these medical interventions, lifestyle modifications play a critical role in managing arthritis symptoms. Patients who embrace a holistic approach that incorporates diet, exercise, and mental well-being often experience improved outcomes.
| Treatment | Osteoarthritis | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
|---|---|---|
| Medications | NSAIDs, Analgesics like acetaminophen, topical pain relievers | DMARDs, Biologics, NSAIDs for pain relief |
| Exercise | Low-impact aerobic activities like swimming and cycling, strength training | Range-of-motion exercises, core strengthening, balance activities |
| Surgery | Joint replacement, arthroscopy to remove debris | Synovectomy or joint replacement, depending on severity |
Managing arthritis joint pain requires a comprehensive and personalized approach. By exploring and combining different treatments like medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and innovative therapies, individuals can achieve improved joint function and a better quality of life. With advancements in research, the future of arthritis treatment holds promise of more effective and innovative solutions for those affected by this chronic condition. Education and awareness about arthritis can empower patients to take an active role in their management, encouraging shared decision-making with healthcare providers. As our understanding of arthritis evolves, so too will our ability to improve the lives of those living with it, paving the way for new horizons in treatment and management strategies.
Explore the Tranquil Bliss of Idyllic Rural Retreats

Ultimate Countdown: The 20 Very Legendary Gaming Consoles Ever!

Understanding Halpin and its Influence

Affordable Full Mouth Dental Implants Near You

Discovering Springdale Estates

Illinois Dentatrust: Comprehensive Overview

Embark on Effortless Adventures: Unveiling the Top in Adventures Made Easy Outdoor Equipment

Unveiling Ossur Valves: Innovation in Prosthetics

Unlock the Full Potential of Your RAM 1500: Master the Art of Efficient Towing!
