Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is increasingly linked to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a primary liver cancer. This article delves into the complex relationship between NAFLD and HCC, exploring its implications for public health. It offers expert insights into diagnosis, management, and prevention strategies to address this growing challenge.
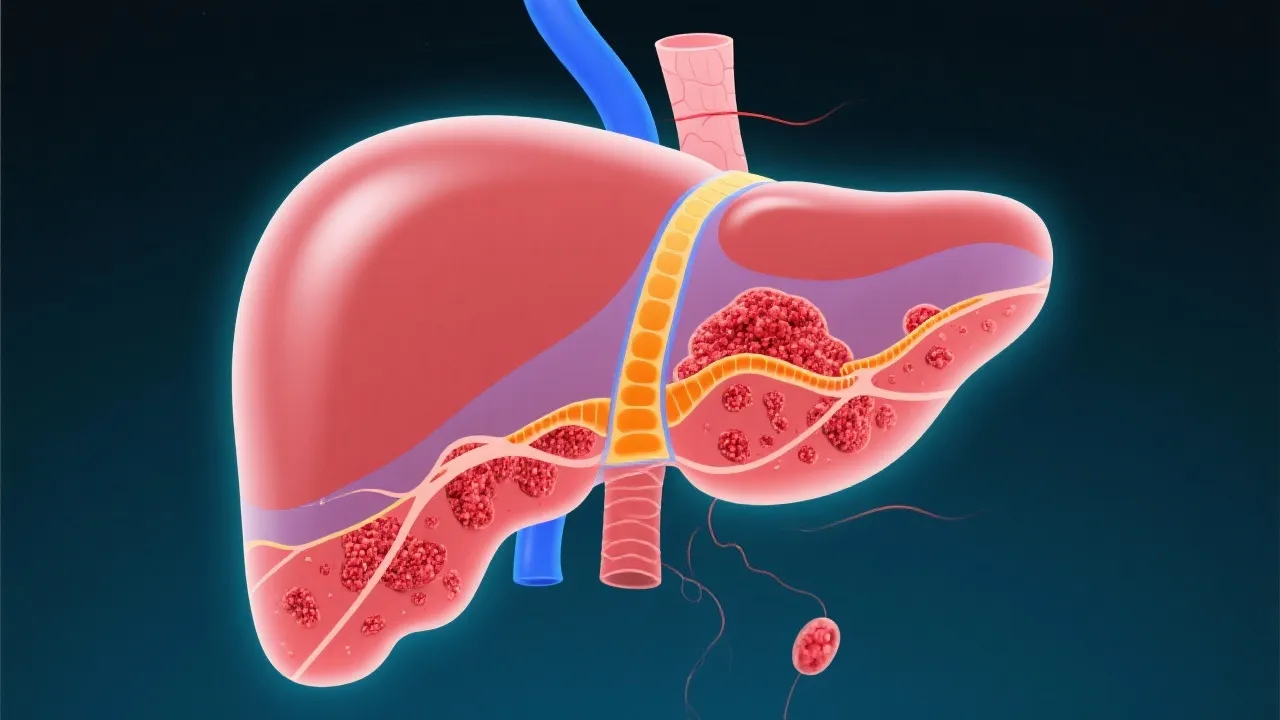
In recent years, the medical community has noticed significant links between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). As obesity and metabolic syndrome become more common globally, NAFLD has emerged as a predominant liver disorder, characterized by excessive fat in liver cells unrelated to alcohol consumption. Concurrently, HCC, the very common primary liver cancer, has started to manifest more frequently, demonstrating a potential epidemiological and pathological link to NAFLD. Recent studies suggest that the prevalence of HCC in patients with established NAFLD is rising, underlining the necessity for ongoing research into preventative measures and treatment modalities. Understanding the association between these two conditions is crucial for the development of effective screening protocols and strategies aimed at reducing morbidity and mortality rates associated with liver disease.
NAFLD encompasses a spectrum of liver conditions, from simple steatosis (fat accumulation) to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), where inflammation and liver cell damage occur. If left unchecked, NASH can progress to cirrhosis and eventually HCC. NAFLD is often asymptomatic, which makes early detection challenging. Patients may remain unaware of the condition until significant liver damage has occurred. The growing understanding of NAFLD is vital, not just for individual patient care, but also for broader public health efforts aimed at combatting the rising obesity epidemic and associated metabolic disorders.
One of the significant challenges in understanding NAFLD lies in its multifactorial nature. It is influenced by genetic predispositions, environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and coexisting medical conditions such as diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension. Research has indicated that the global increase in caloric intake, along with sedentary lifestyles, contributes heavily to the rising rates of NAFLD. It is also noteworthy that certain populations, including those with a genetic predisposition, may be at particularly high risk.
The pathogenesis of NAFLD-related HCC involves a complex interplay of genetic, metabolic, and inflammatory factors. Insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and the release of inflammatory cytokines contribute to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and ultimately, carcinogenesis. Due to the insidious nature of NAFLD, many patients may remain undiagnosed for years, allowing the disease to progress unchecked. The transition from NAFLD to NASH is particularly critical, as inflammation and fibrosis in the liver substantially increase the risk of developing HCC.
Several key mechanisms have been proposed to explain the progression from NAFLD to HCC. For instance, the accumulation of fat in liver cells triggers a cascade of metabolic dysregulation leading to cellular stress. This stress promotes inflammation and triggers the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-alpha and interleukin-6, which contribute to liver cell injury. Excessive fat also leads to the formation of reactive oxygen species, causing oxidative damage to hepatocytes. Over time, the combination of these factors results in fibrosis, which is associated with an increased risk of malignancy.
Genetics also plays a pivotal role in determining an individual’s risk for developing NAFLD and, subsequently, HCC. Genetic variations in pathways regulating lipid metabolism, inflammation, and fibrosis can significantly affect disease outcomes. Furthermore, ongoing research is exploring how epigenetic modifications—changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations to the underlying DNA sequence—may influence susceptibility to liver disease and cancer progression.
Diagnosing NAFLD and its progression to HCC involves a combination of imaging, liver function tests, and biopsy. However, the silent nature of NAFLD often leads to late-stage diagnosis, when symptoms become evident. As a result, many patients are diagnosed only after significant liver damage has already occurred, often coinciding with the onset of complications associated with cirrhosis or HCC. Recent advancements in non-invasive diagnostic tools, such as transient elastography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), offer promising avenues for early detection and monitoring.
Transient elastography, commonly referred to as FibroScan, measures liver stiffness, which correlates with the degree of fibrosis. The ability to assess liver stiffness non-invasively and rapidly makes this technique a valuable tool in the routine evaluation of patients at risk for NAFLD and HCC. MRI is particularly beneficial for assessing liver fat content and characterizing hepatic lesions, which is crucial for differentiating between benign and malignant nodules in patients with a history of liver disease.
While imaging techniques have made significant strides, there is still a crucial need for effective biomarkers that can predict fibrosis progression and cancer development in patients with NAFLD. Ongoing research efforts are focused on identifying specific serum biomarkers or panels that correlate with disease severity and can be utilized for prognostic purposes.
The rising prevalence of HCC linked to NAFLD has been observed worldwide, with varying rates across regions. Developed countries show higher incidence rates due to lifestyle-associated risk factors, while developing nations observe increasing trends as urbanization influences lifestyle changes. A transition from traditional diets to high-calorie, processed foods mirrors increases in obesity rates globally, resulting in a parallel surge in liver diseases, including NAFLD and HCC.
A comprehensive understanding of global epidemiological trends can assist policymakers in resource allocation and the development of targeted interventions. Countries with rising obesity rates must prioritize public health measures aimed at obesity prevention, enhancing healthcare access for early diagnosis and treatment of NAFLD. Additionally, health education campaigns that raise awareness about liver health can contribute to improved outcomes and decreased disease incidence.
Regionally, certain populations may experience higher incidences of NAFLD-related HCC due to unique genetic and environmental factors. For example, studies have indicated that Asian populations exhibit higher susceptibility due to variations in genetic predispositions affecting fat deposition and inflammatory responses. Understanding these region-specific trends facilitates the customization of public health strategies tailored to the needs of diverse populations.
Addressing NAFLD and preventing its progression to HCC necessitates lifestyle modifications. Weight loss, regular physical activity, and dietary changes can significantly impact liver health. Studies have demonstrated that even modest weight loss can lead to improvements in liver histology and may reverse the progression of fibrosis in patients with NASH. Additionally, nutritional interventions focusing on a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins support healthy liver function.
In recent years, the concept of a Mediterranean diet has gained popularity for its protective effects on liver health, showing potential in reducing steatosis and fibrosis. This diet emphasizes the consumption of healthy fats, particularly from olive oil and fish, and limits the intake of refined sugars and carbohydrates. Incorporating physical activity, such as aerobic exercises and resistance training, further enhances the effectiveness of lifestyle modifications.
Medical interventions, including the use of insulin sensitizers and lipid-lowering agents, further aid in disease management. Agents such as pioglitazone, a thiazolidinedione, have proven benefits in reducing liver inflammation and fibrosis. Other pharmacological options are currently under investigation, including GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors, which show promise in managing metabolic syndrome components associated with NAFLD. Furthermore, ongoing trials aim to validate the effectiveness of specific drugs in halting the disease progression and lowering the incidence of HCC.
Treatment options for HCC in NAFLD patients include surgical resection, liver transplant, and locoregional therapies like radiofrequency ablation. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including tumor stage, liver function, and patient health. Resection is typically reserved for those with single tumors and preserved liver function, while liver transplantation is an option for patients with advanced disease and significant cirrhosis.
Locoregional therapies, such as radiofrequency ablation and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), provide alternatives for patients who are not candidates for surgery. These approaches aim to reduce tumor burden and improve survival rates. Systemic therapies, such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (e.g., sorafenib and lenvatinib) and immunotherapy, are also emerging in managing advanced-stage HCC. The current landscape of HCC treatment is rapidly evolving, with ongoing clinical trials designed to explore combination therapies and novel agents that can enhance treatment efficacy.
As the medical community continues to better understand the interactions between NAFLD and HCC, the need for personalized treatment plans becomes increasingly evident. Factors such as individual metabolism, genetic background, and the presence of comorbid conditions must be considered, allowing healthcare providers to tailor treatment strategies to meet specific patient needs effectively.
Ongoing research focuses on understanding the pathophysiological links between NAFLD and HCC to enhance therapeutic approaches. Emerging fields such as genomics, metabolomics, and microbiome studies offer new insights into potential targets for intervention. Recent advancements in molecular biology techniques have enabled researchers to explore the complex interplay of gut microbiota, systemic inflammation, and metabolic dysregulation more comprehensively. Studies have suggested that alterations in gut microbiota may contribute to the progression of NAFLD and its transition to HCC, highlighting the potential for microbiome-targeted therapies.
Furthermore, clinical studies investigating the efficacy of novel pharmacological agents are crucial for establishing evidence-based guidelines for managing patients with NAFLD and HCC. Collaborative efforts between scientists, healthcare providers, and policymakers are essential to address this growing healthcare burden. With the increasing recognition of the social determinants of health, integrating multidisciplinary, community-based approaches into liver disease management has also proven to be vital for effective interventions.
Future directions in research must also focus on the development of comprehensive screening protocols for at-risk populations. Identifying high-risk individuals early can lead to timely interventions, potentially altering the disease trajectory. Implementing regular screening for NAFLD in populations with prevalent risk factors, combined with public health campaigns promoting obesity prevention, can considerably reduce the burden of NAFLD-related HCC.
| Condition | Features |
|---|---|
| NAFLD | Characterized by excess liver fat, no significant alcohol consumption, linked to obesity and metabolic syndrome. Represents the initial phase of liver disease with potential progression to more severe forms. |
| NASH | Advanced form of NAFLD, involving liver inflammation and damage, precursor to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Represents a critical stage where intervention can significantly alter outcomes. |
| HCC | Primary liver cancer, arises in the context of chronic liver diseases like cirrhosis, increasingly linked to NAFLD. Represents end-stage liver disease with complex treatment challenges. |
The management of NAFLD and NAFLD-related HCC requires comprehensive approaches:
NAFLD is primarily caused by lifestyle factors such as poor diet and lack of exercise, often linked to obesity and metabolic syndrome. In addition to lifestyle, genetic predispositions and environmental factors also play a significant role in its development.
Diagnosis usually involves imaging techniques like ultrasound, elastography, and MRI, supplemented with liver function tests. A thorough patient history and physical examination are also critical components of the diagnostic process.
Prevention focuses on lifestyle interventions, managing risk factors, and regular screening in at-risk populations. For patients with established NAFLD, proactive management of metabolic syndrome components and routine monitoring can help mitigate the risk of HCC.
Treatment varies based on the disease stage, including surgical resection, liver transplant, ablation techniques, and systemic therapies. The choice of treatment is highly individualized and considers the patient’s overall health, liver function, and tumor characteristics.
Genetic predispositions may influence susceptibility, with ongoing research to identify specific genetic markers. Understanding these variations could pave the way for personalized treatment strategies in NAFLD and HCC.
The intertwining of NAFLD and HCC presents a complex challenge for contemporary healthcare, demanding a multifaceted approach to diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. As the incidence of both conditions continues to rise, proactive public health strategies are essential for addressing the ever-increasing burden on healthcare systems. By understanding the underlying mechanisms, implementing preventive measures, and fostering advancements in treatment protocols, we can significantly mitigate the impact of these conditions on global health. In doing so, it is vital to involve a broad array of stakeholders, including healthcare professionals, researchers, and policymakers, to create comprehensive frameworks for effective management and education regarding NAFLD and HCC.
Explore the Tranquil Bliss of Idyllic Rural Retreats

Ultimate Countdown: The 20 Very Legendary Gaming Consoles Ever!

Understanding Halpin and its Influence

Affordable Full Mouth Dental Implants Near You

Discovering Springdale Estates

Illinois Dentatrust: Comprehensive Overview

Embark on Effortless Adventures: Unveiling the Top in Adventures Made Easy Outdoor Equipment

Unveiling Ossur Valves: Innovation in Prosthetics

Unlock the Full Potential of Your RAM 1500: Master the Art of Efficient Towing!
