This guide delves into the complexities of liver transplantation due to NASH (Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis), a significant cause of liver disease that may require transplantation. It explores how NASH can lead to cirrhosis, the intricacies of the transplantation process, and offers an expert perspective on current challenges, statistics, and advancements in liver transplantation.
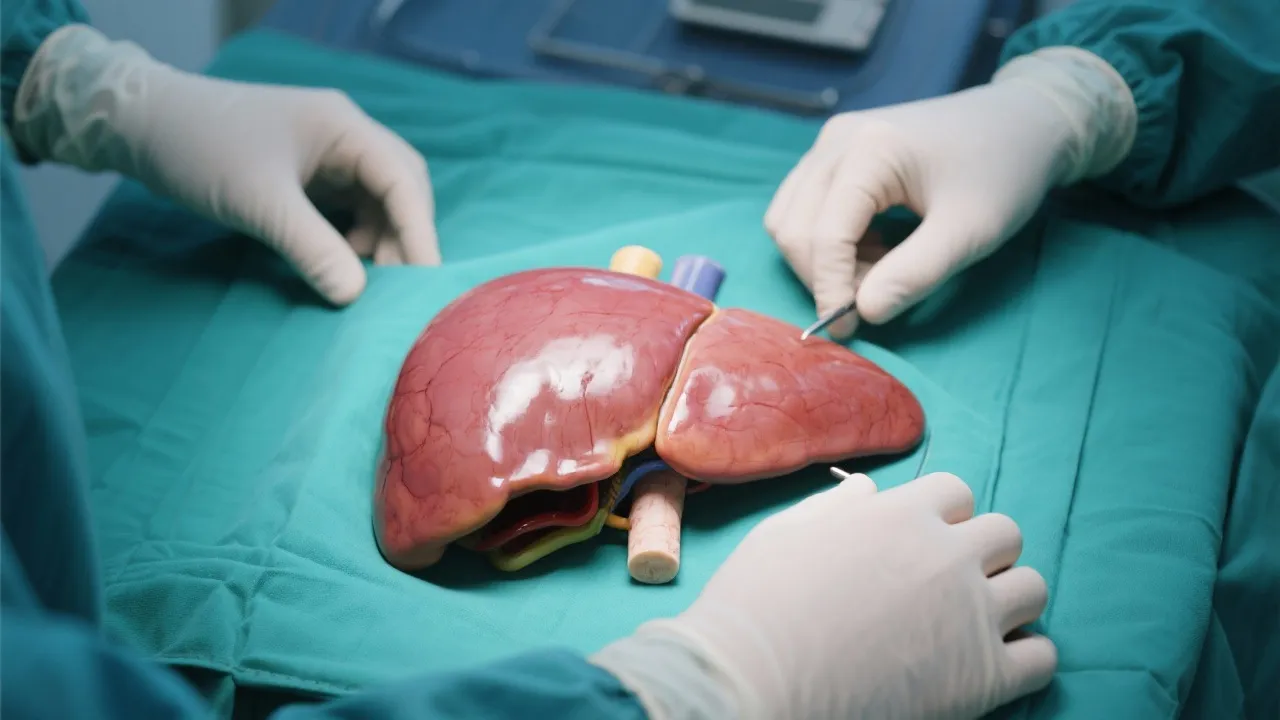
Liver transplantation has become a critical medical procedure for patients with severe liver diseases, including those caused by Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). NASH, an advanced form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), leads to liver inflammation and damage and can progress to cirrhosis. This necessitates the need for a liver transplant, where the damaged liver is replaced with a healthy one from a donor.
The impact of liver disease on patient health and quality of life can be profound. Conditions such as NASH not only threaten vital liver functions but can lead to debilitating symptoms, fatigue, jaundice, and swelling. Furthermore, individuals with advanced liver diseases often face social stigmas associated with liver disease, particularly when it comes to alcohol-related conditions. Thus, understanding and addressing liver transplantation is not only a medical concern but also a significant aspect of patient advocacy and support.
NASH is characterized by fat accumulation, liver cell injury, and inflammation. As mentioned, with lifestyle changes such as increased sugar consumption and reduced physical activity, NASH has become one of the fastest-growing causes of liver disease, eventually leading to cirrhosis. The transition from NAFLD to NASH is marked by an inflammatory response that results in additional scarring or fibrosis of the liver. This condition not only impairs liver function but also increases the risk of liver cancer.
Research insights indicate that nearly 25% of individuals with NASH may eventually progress to cirrhosis. It is alarming to note that NASH-related cirrhosis can mimic the symptoms of alcohol-related cirrhosis despite occurring in individuals who do not consume alcohol. The fibrosis associated with NASH is not only related to the presence of fat in the liver but also linked to genetic and metabolic factors, including obesity, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia.
As the demand for liver transplants rises, understanding the connection between NASH and its impact on liver health is crucial. Increased awareness can prompt early intervention strategies aimed at addressing lifestyle risk factors and potentially halting disease progression before transplantation becomes necessary. Moreover, public health initiatives aimed at combating rising obesity and promoting healthier lifestyles are critical to decreasing NASH prevalence.
The liver transplantation process is intricate and involves several stages. Firstly, pre-transplant evaluations include thorough medical exams to ensure patient suitability and compatibility with donor organs, which is crucial to minimize the risk of rejection. This step often requires a multidisciplinary team approach including hepatologists, transplant surgeons, and nutritionists to assess the overall health of the patient.
Once a viable liver becomes available, its recovery and surgical transplantation are undertaken by specialized teams. The transplantation itself involves several key steps. Surgeons first remove the diseased liver, and then the new donor liver is connected to the body's vascular and biliary systems. The surgery typically lasts between 6 to 12 hours, depending on the complexity of the case. Following surgery, patients are monitored in a specialized transplant unit where their recovery begins.
Post-surgery, patients require a lifetime of regular check-ups and medications to prevent organ rejection. Immunosuppressants are critical in the immediate post-operative phase and throughout the patient's life to reduce the risk of the immune system attacking the transplanted liver. Education about medication compliance, potential side effects, and lifestyle modifications play essential roles in ensuring a successful transplantation journey.
Liver transplantation for NASH presents unique challenges. Due to rising obesity rates, the pool of eligible donors is decreasing, leading to longer waiting lists. Patients with NASH often have comorbid conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and hypertension, complicating post-transplant care and increasing the risk of adverse outcomes. Thus, the management of these comorbid conditions before and after transplantation becomes a focal point for healthcare providers.
There is also the concerning issue of metabolic syndrome, which represents a cluster of conditions, including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels. Patients with metabolic syndrome are at higher risk of complications during and after liver transplantation, including increased rates of infection and reduced graft function.
Moreover, there is the risk of recurrent NASH damaging the new liver. Evidence suggests that a significant proportion of individuals who previously had NASH may experience a recurrence after transplantation, which can lead to progressive liver injury and, ultimately, a compromised graft. This underscores the necessity for ongoing research into effective management strategies and preventive measures post-transplant. Research into pharmacological interventions targeting NASH and lifestyle changes focused on weight loss and nutrition may be pivotal in improving outcomes for these patients.
Recent advancements are helping to improve liver transplantation outcomes. Innovations in surgical techniques, better immunosuppressive drugs, and improved donor matching processes have significantly increased survival rates. For instance, the development of living-donor liver transplantation allows for a more expansive donor pool, as a portion of a healthy liver from a living donor can be transplanted into a recipient, which can dramatically shorten wait times and improve outcomes.
Moreover, advancements in immunosuppressive therapy, including the introduction of new classes of medications that minimize toxicity and maximize graft protection, have shown promise in reducing rates of rejection and other complications post-transplant. These medical advancements necessitate continuous education for patients, enabling them to make informed choices about their treatment options and adhere to medical regimens that enhance their health.
Emerging therapies targeting NASH directly aim to reduce the burden on the liver transplant system by managing the root cause. Innovative agents, including those targeting insulin resistance, inflammatory pathways, and fibrosis development, are under investigation. Clinical trials evaluating these therapies are vital, as they may provide effective alternatives to liver transplantation in the future, particularly for earlier-stage NASH patients.
While liver transplantation can be life-saving, it is also associated with long-term considerations for patients. Studies have shown improved overall survival rates, but the quality of life post-transplant is an equally critical area of analysis. Patients often report significant improvements in their quality of life and ability to return to normal activities following a successful transplant.
However, life after transplantation requires vigilant long-term follow-up and health management. Routine monitoring of liver function, screening for liver cancer, and managing comorbid conditions become integral parts of a transplant recipient’s life. Additionally, transplant patients may experience psychological effects such as anxiety and depression, necessitating mental health support. Therefore, comprehensive care models that integrate physical health, mental health, and social support are crucial for optimizing long-term outcomes for liver transplant recipients.
Education is a key component in the successful management of patients with NASH and those who undergo liver transplantation. Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in educating patients about the nature of their disease, potential complications, and the life-long commitment required for managing their health post-transplant. This education should encompass topics related to medication adherence, diet modifications, physical activity, and the importance of regular medical follow-ups.
Support systems, including organized patient groups, can offer invaluable resources. These groups often provide emotional support, practical advice, and shared experiences from others who have undergone similar journeys. The sense of community fosters hope and offers individuals a platform to discuss challenges. Creating a robust network of support, including family members, healthcare providers, and peer supporters, can greatly enhance the coping strategies and resilience of patients recovering from transplantation.
Liver transplantation for NASH patients remains a complex yet essential medical intervention. The rising prevalence of NASH requires a multi-faceted approach that combines early diagnosis, lifestyle modifications, medical advancements, and ongoing research. The integration of patient education and robust support systems plays a crucial role in enhancing post-transplant outcomes and quality of life.
As we move forward, the emphasis on understanding the pathophysiology of NASH will open new avenues for treatment, potentially reducing liver transplant demands. Collaborative efforts between researchers, healthcare providers, and patients will be vital in improving overall care strategies, ultimately leading to better management of liver diseases associated with NASH and supporting those who are awaiting life-saving transplants.
Investment in awareness campaigns aimed at educating the public about liver health and NASH can also be instrumental in combating the root causes of this escalating health issue. With dedication and continued innovation, improving patient outcomes for those with NASH and requiring liver transplants can be achieved, paving the way for healthier futures.
Explore the Tranquil Bliss of Idyllic Rural Retreats

Ultimate Countdown: The 20 Very Legendary Gaming Consoles Ever!

Understanding Halpin and its Influence

Affordable Full Mouth Dental Implants Near You

Discovering Springdale Estates

Illinois Dentatrust: Comprehensive Overview

Embark on Effortless Adventures: Unveiling the Top in Adventures Made Easy Outdoor Equipment

Unveiling Ossur Valves: Innovation in Prosthetics

Unlock the Full Potential of Your RAM 1500: Master the Art of Efficient Towing!
