This article delves into the relationship between Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). NAFLD is a common liver condition not associated with alcohol abuse, often leading to liver inflammation and damage. Understanding its progression to HCC provides crucial insights into prevention, diagnosis, and treatment strategies pivotal for patient outcomes.
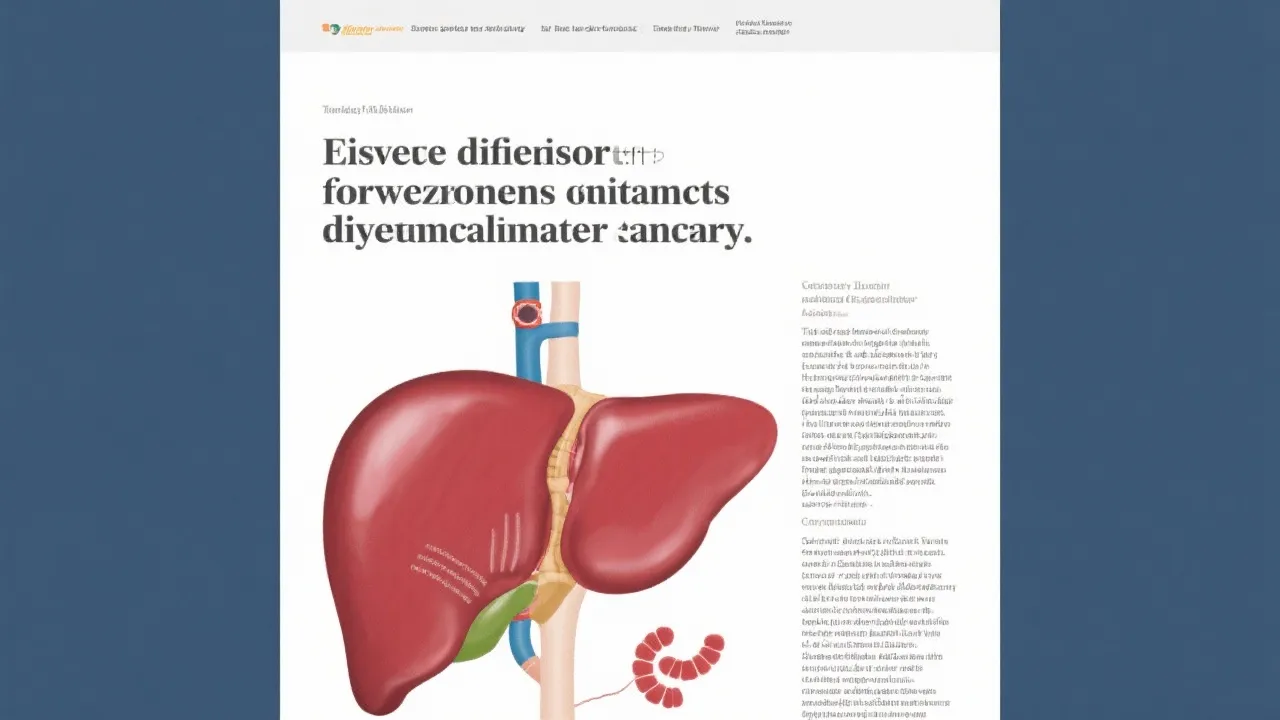
Liver diseases encompass a broad range of conditions, with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) being one of the very prevalent worldwide. NAFLD primarily manifests as excess fat accumulation in the liver, not attributable to significant alcohol consumption. One of the severe implications of NAFLD is its progression to Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC), a primary liver cancer type that poses significant health challenges globally. This dynamic underscores the importance of understanding the multifaceted nature of liver diseases and their potential pathways from benign to malignant states.
NAFLD is a significant health concern characterized by the build-up of extra fat in liver cells in individuals who consume little to no alcohol. This condition is closely associated with obesity, diabetes, insulin resistance, and other metabolic syndromes. NAFLD can develop into a more severe form known as Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), which involves liver inflammation and damage, potentially leading to cirrhosis or liver cancer over time. The epidemiology of NAFLD indicates a global prevalence that reflects the increasing rates of obesity and sedentary lifestyles in modern society. Notably, it is estimated that nearly 25% of the global population may have NAFLD, with varying degrees of severity.
The journey from NAFLD to HCC involves several stages and risk factors. As liver damage progresses from simple steatosis (fat accumulation) to steatohepatitis (fat with inflammation) and fibrosis, the risk of developing cirrhosis increases. Cirrhosis, or severe scarring of the liver tissue, significantly raises the probability of hepatocellular carcinoma. Research indicates that approximately 20% of patients with NASH will progress to cirrhosis over a period of 10-20 years. Importantly, not all patients with NAFLD will progress to HCC, but those with additional risk factors, such as age and genetic predisposition, may experience a faster progression. Attention to metabolic risk factors and early intervention is crucial to prevent this evolution.
Diagnosing NAFLD and tracking its progression involves various methods, ranging from blood tests that measure liver enzymes to imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI. A liver biopsy may be necessary to distinguish between NAFLD and NASH. Recent advancements in non-invasive diagnostic methods, such as elastography and serum biomarkers, allow for better identification of liver stiffness and inflammation, reducing the need for invasive procedures. Regular monitoring and early detection of liver changes can prompt timely interventions, potentially staving off HCC development. It is essential for healthcare professionals to remain vigilant in screening high-risk populations, particularly those exhibiting metabolic syndrome characteristics.
Managing NAFLD and its potential progression to HCC involves lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Weight loss, healthy diet, and physical activity are primary strategies for those at risk. Studies have demonstrated that even modest weight loss (5-10% of body weight) can significantly reduce liver fat and inflammation. In cases where NASH is diagnosed, medications to control diabetes, reduce lipids, and protect the liver may be prescribed. Ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the effectiveness of various pharmacological agents, including vitamin E and pioglitazone, in treating NASH. For patients who progress to HCC, treatment options include surgical resection, liver transplantation, chemotherapy, and emerging therapies like immunotherapy. The choice of treatment often depends on the stage of the disease, liver function, and overall patient health, requiring a multidisciplinary approach for optimal outcomes.
Research is crucial in understanding the complex interactions between NAFLD and HCC. Ongoing clinical trials focus on innovative therapies targeting metabolic pathways and exploring genetic predispositions that might influence disease progression. For instance, studies are examining the role of the gut microbiome in NAFLD progression, potentially opening new avenues for therapeutic interventions through dietary modifications or probiotics. Engaging with clinical research not only improves treatment protocols but also enhances patient care strategies. By developing novel pharmacotherapies and refining clinical management pathways, researchers aim to address both the burden of NAFLD and its malignant transformation into HCC.
The increasing prevalence of NAFLD poses significant public health challenges, demanding comprehensive awareness programs and policy changes. Educating healthcare providers and the public about lifestyle risk factors and the importance of early diagnosis can play a pivotal role in mitigating the burden of liver-related illnesses. Public health initiatives aimed at reducing obesity rates through community-based dietary programs and exercise regimens have become essential components in tackling this epidemic. Moreover, investment in research and funding for liver disease education ensures that the medical community is equipped to handle the growing incidence of NAFLD and its related complications. Collaborative efforts between governmental bodies, healthcare organizations, and educational institutions are necessary to foster environments that promote better liver health.
Despite the progress made in understanding NAFLD and its link to HCC, several challenges remain in effective management and treatment. One significant issue is the lack of standardized diagnostic criteria and treatment protocols, which can lead to inconsistent patient care. Additionally, there is often a general lack of awareness among both healthcare providers and patients regarding the severity and implications of NAFLD. Addressing these gaps requires concerted efforts in education and standardized practices. The development of clear guidelines by reputable medical organizations is essential to promote uniform care approaches.
As we move forward, integrating technology into NAFLD management presents exciting opportunities. Digital health tools, such as mobile applications for tracking dietary habits and physical activity levels, can empower patients to take charge of their health. Telemedicine is also emerging as a pragmatic solution for increasing access to expert consultations, particularly in remote areas where healthcare resources are limited. These tools, when used effectively, can enhance patient engagement, ensure adherence to treatment plans, and provide real-time monitoring, potentially leading to improved health outcomes.
Another promising direction in managing NAFLD and its complications involves integrative and holistic approaches. These methods emphasize the importance of addressing not only the physical manifestations of liver disease but also the psychological and social factors that contribute to health. Mindfulness practices, stress management, and behavioral therapies can be beneficial in promoting healthier lifestyles. Additionally, community support systems can provide the encouragement necessary for individuals to maintain lifestyle changes, thereby enhancing overall health and well-being.
Understanding NAFLD and its potential evolution to HCC is crucial in crafting effective prevention and treatment strategies. With burgeoning research and focused healthcare initiatives, strides can be made in reducing the incidence and impact of these liver diseases, ultimately improving patient quality of life and outcomes. As the landscape of liver disease continues to evolve, a collaborative effort among healthcare professionals, researchers, and policymakers is essential. It is through comprehensive awareness, advanced research, and innovative treatment strategies that we can hope to combat the rising threat of liver diseases, ensuring that affected individuals receive the best possible care and support.
Explore the Tranquil Bliss of Idyllic Rural Retreats

Ultimate Countdown: The 20 Very Legendary Gaming Consoles Ever!

Understanding Halpin and its Influence

Affordable Full Mouth Dental Implants Near You

Discovering Springdale Estates

Illinois Dentatrust: Comprehensive Overview

Embark on Effortless Adventures: Unveiling the Top in Adventures Made Easy Outdoor Equipment

Unveiling Ossur Valves: Innovation in Prosthetics

Unlock the Full Potential of Your RAM 1500: Master the Art of Efficient Towing!
