Hepatitis E is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis E virus (HEV), primarily transmitted through the consumption of contaminated water or food. While the infection is usually self-limiting, it can lead to severe liver complications particularly in pregnant women and people with pre-existing liver conditions. In rare cases, infection may result in acute liver failure necessitating a liver transplant. This article explores the relationship between hepatitis E and liver transplants, providing insights into when and why a transplant may be necessary, as well as the procedure involved.
Hepatitis E is a viral infection that primarily impacts the liver, caused by the hepatitis E virus (HEV). This infection is characterized by its predominant mode of transmission through the fecal-oral route, especially via contaminated water supplies. Hepatitis E is a significant health concern in many parts of the world, particularly in regions with inadequate sanitation and hygiene. The virus is particularly prevalent in developing countries, where outbreaks can lead to larger public health crises.
The majority of hepatitis E cases result in acute infections, such as mild symptoms including jaundice, fatigue, and nausea, which typically resolve spontaneously without any medical intervention. However, in certain vulnerable populations, HEV can lead to severe complications, including acute liver failure, which is a critical condition that may necessitate a liver transplant. Understanding the dynamics of hepatitis E can help strengthen public health responses and preventative measures to reduce the burden of this disease.
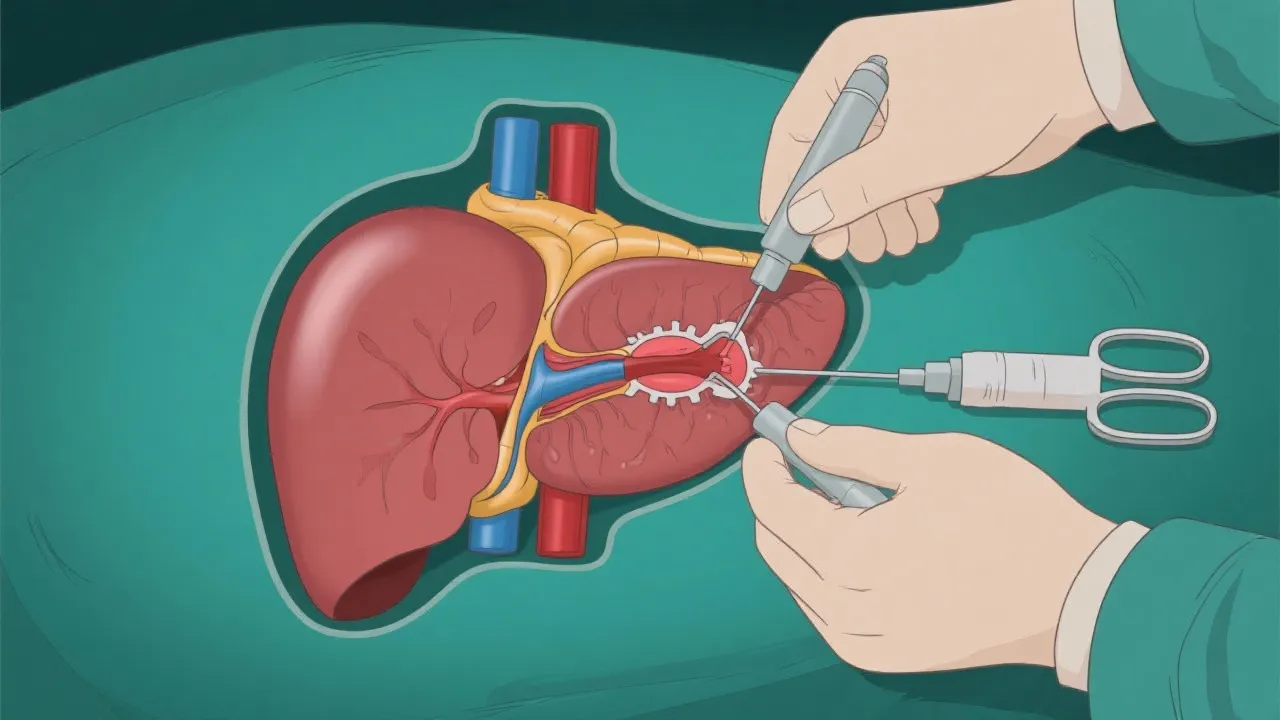
A liver transplant is a surgical procedure that involves replacing a diseased liver with a healthy liver from a donor. This procedure is often considered when the liver no longer functions adequately due to various underlying causes such as chronic liver diseases, acute liver failure, or inherited metabolic disorders. The liver performs essential functions, including detoxifying harmful substances, producing bile for digestion, and storing nutrients, among others. It has a remarkable ability to regenerate, but when irreparable damage occurs, transplantation becomes a vital treatment option.
While liver transplants are commonly associated with chronic liver diseases like cirrhosis, they are also crucial for acute liver failure, including those cases triggered by hepatitis E. The surgical procedure involves an extensive preoperative evaluation, wherein the patient is assessed to determine their eligibility for the transplant. This evaluation considers the liver’s severity, the patient’s general health, and the presence of any comorbid conditions. A successful liver transplant can significantly improve the quality of life and survival rates of patients facing severe liver dysfunction.
Although most individuals infected with hepatitis E experience mild symptoms, some populations are more susceptible to severe liver complications. Pregnant women, especially those in their third trimester, face an elevated risk of developing fulminant hepatic failure due to hepatitis E. Research suggests that this increased vulnerability may be due to alterations in the immune response that occur during pregnancy. Data indicate that the mortality rate among pregnant women with hepatitis E can reach as high as 20-25%, underscoring the need for close monitoring and proactive management.
Individuals with pre-existing liver diseases, such as chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis, also face a higher risk of severe outcomes when infected with hepatitis E. These risks are compounded when patients have additional factors such as alcohol use, obesity, or diabetes. In circumstances where hepatitis E progresses to acute liver failure, the onset of symptoms can be rapid, and a liver transplant may be necessary. The decision to pursue a transplant is multifaceted, requiring a collaborative approach among a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals—including hepatologists, surgeons, transplant coordinators, and nursing staff—to assess the patient's condition comprehensively.
Liver transplant procedures involve several stages, beginning with the identification of a suitable donor. Donors can be living or deceased, but in both cases, compatibility is paramount to ensure the success of the transplant. Various factors are considered for compatibility, including blood type, body size, and the urgency of the recipient's condition. Living liver donors typically donate a portion of their liver, which can regenerate over time. This option may accelerate the transplantation process and reduce waiting times associated with deceased donor lists.
The surgical procedure itself is technically demanding, requiring highly specialized medical expertise and advanced surgical facilities. Below are the primary stages involved in a liver transplant:
| Stages of Liver Transplant | Details |
|---|---|
| Evaluation | A comprehensive evaluation of the patient's health, including blood tests, imaging tests, and psychological assessments to establish readiness for transplantation. |
| Donor Matching | Finding a compatible donor. Compatibility is based on blood type, body size, and the urgency of the recipient's condition. The matching process is pivotal for transplant success. |
| Surgery | Removal of the diseased liver and replacement with the donor liver. This is a complex surgery requiring skilled healthcare personnel and can last several hours. During this time, the surgical team must also ensure that blood flow remains stable and that the new liver is functioning optimally. |
| Recovery | Post-operative care is critical, including monitoring for signs of rejection and managing medications to prevent infection. Patients typically begin rehabilitation efforts within a few days post-surgery, focused on regaining strength and independence. |
While liver transplants can be life-saving, various challenges are associated with the procedure. One of the foremost challenges is the need for lifelong immunosuppressive therapy post-transplant. Patients must take these medications to prevent organ rejection, but they must also contend with a heightened risk of infections and other complications. These medications require careful monitoring to balance the risk of rejection with the risk of infection, making an ongoing relationship with healthcare providers essential.
Furthermore, the availability of donor organs remains a significant challenge in many countries. The disparity between the number of patients awaiting transplants and the available organs often leads to long waiting periods, with some patients becoming too ill to undergo surgery before an organ becomes available. This concern propels ongoing research into artificial organs, xenotransplantation, and methods to expand the donor pool, such as living donor liver transplants.
Despite these challenges, success rates for liver transplants are relatively high. According to various studies, one-year survival rates post-transplant can exceed 90%, and five-year survival rates are around 75% or higher, dependent on factors such as the underlying condition of the liver and the patient’s general health at the time of transplantation. Constant advancements in surgical techniques, organ preservation, and post-operative care continue to improve patient outcomes. Many recipients can return to a good quality of life after recovery, engaging in normal activities and experiencing improved health.
After a liver transplant, the importance of post-operative care and lifestyle changes cannot be overstated. Patients should be vigilant about adhering to their medication regimen to manage their immune system effectively and prevent rejection of the new organ. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor liver function and adjust medications as needed. These appointments typically include blood tests and imaging studies to ensure the transplant is functioning well and to check for any signs of complications.
In addition to routine medical assessments, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in the long-term success of a liver transplant. Patients are generally advised to maintain a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, and avoid substances that can harm the liver, such as alcohol and certain medications. Nutritional counseling is often provided to help patients understand how to support their liver health while managing any underlying conditions like diabetes or hypertension.
Support systems, including family and peer groups, can significantly enhance the patient’s emotional wellbeing during recovery. Many transplant centers offer counseling services and support groups that help patients navigate the psychological aspects of coping with their illness, the transplant process, and the ongoing lifestyle adjustments. Addressing mental health is equally important, as emotional resilience can impact the recovery journey positively.
The implications of liver disease and the need for liver transplants extend beyond individual patients; they have significant social and economic ramifications. Chronic liver disorders and complications from hepatitis E can lead to a substantial burden on healthcare systems, evidenced by increased hospitalizations, extended treatment times, and the need for ongoing medical care.
Economically, the costs associated with liver transplants can be staggering. They typically include not just the surgery itself but also all pre-operative evaluations, post-operative care, and long-term follow-up treatments. As such, many patients may face financial challenges, particularly in regions where health insurance coverage is limited. The financial strain can be exacerbated by lost productivity during periods of illness and recovery. As a result, addressing the prevention of hepatitis E and promoting liver health can significantly alleviate the overall burden on both patients and health systems.
On a broader scale, public health initiatives targeting sanitation and clean water access can lead to substantial reductions in hepatitis E transmission and liver disease burden. Strengthening public health infrastructure, increasing awareness about hepatitis E transmission, and investing in preventive measures can have profound impacts on community health and economic stability.
Preventing hepatitis E entails a multifaceted approach that includes improving sanitation and cleanliness, ensuring the safety of drinking water, and promoting proper hygiene practices. Public education aimed at raising awareness about the risks of waterborne diseases and the importance of safe food handling can help mitigate outbreaks. In many developing countries, interventions such as the provision of clean drinking water and sanitation facilities can have a remarkable impact on reducing the incidence of hepatitis E.
Vaccination represents another promising avenue for hepatitis E prevention. Currently, there is a vaccine available in some countries, which has shown efficacy in clinical trials and provides a potential means to control outbreaks effectively. Ongoing research is critical, with efforts focusing on understanding the immune response elicited by vaccination and determining long-term immunity duration.
As research continues, there is a growing emphasis on developing therapeutic strategies that may be useful for managing hepatitis E, especially in high-risk populations. This includes studying antiviral agents that can reduce viral load, limit disease progression, and ultimately improve outcomes for those infected with the virus.
What is the primary cause of hepatitis E?
Hepatitis E is primarily caused by consuming contaminated water or food, often linked to inadequate sanitation and hygiene practices.
Who is very at risk for severe complications from hepatitis E?
Pregnant women, particularly in their third trimester, and individuals with pre-existing liver conditions face higher risks. Other high-risk groups include older adults and immunocompromised individuals.
Is a liver transplant always necessary for hepatitis E cases?
No, a liver transplant is only necessary if the infection leads to acute liver failure, which is rare, occurring in only a small percentage of patients.
What are the success rates of liver transplants?
Success rates are generally high, with many recipients experiencing a significant improvement in their quality of life and overall health following transplantation.
How long is the recovery period after a liver transplant?
Recovery can vary but generally involves several months of rehabilitation and medical care to monitor for complications. Full recovery can take up to a year, during which patients may gradually resume normal activities.
What are some warning signs of liver complications post-transplant?
Patients should be alert for signs of potential complications, such as jaundice, severe fatigue, abdominal pain, fever, or any sudden change in health status. Prompt communication with healthcare providers is crucial for managing any issues that may arise.
Ultimately, while hepatitis E is typically a mild illness for the majority, it underscores the critical role of liver transplants for the minority who experience severe complications. Proper awareness, timely intervention, and advanced surgical methods offer hope and a significantly improved quality of life for those requiring such procedures. Continuous public health efforts to enhance sanitation and hygiene remain essential in reducing the incidence of hepatitis E, thereby lowering the need for liver transplants resulting from this viral infection.
Explore the Tranquil Bliss of Idyllic Rural Retreats

Ultimate Countdown: The 20 Very Legendary Gaming Consoles Ever!

Understanding Halpin and its Influence

Affordable Full Mouth Dental Implants Near You

Discovering Springdale Estates

Illinois Dentatrust: Comprehensive Overview

Embark on Effortless Adventures: Unveiling the Top in Adventures Made Easy Outdoor Equipment

Unveiling Ossur Valves: Innovation in Prosthetics

Unlock the Full Potential of Your RAM 1500: Master the Art of Efficient Towing!
