Eczema, commonly interlinked with atopic dermatitis, impacts numerous individuals globally. Characterized by inflamed, itchy skin, this condition is prevalent and can affect quality of life. Our in-depth analysis provides insights into its causes, symptoms, management strategies, and essential guidelines for those affected or seeking to understand more about this dermatological issue. With expert advice, discover effective ways to alleviate discomfort and enhance skin health.
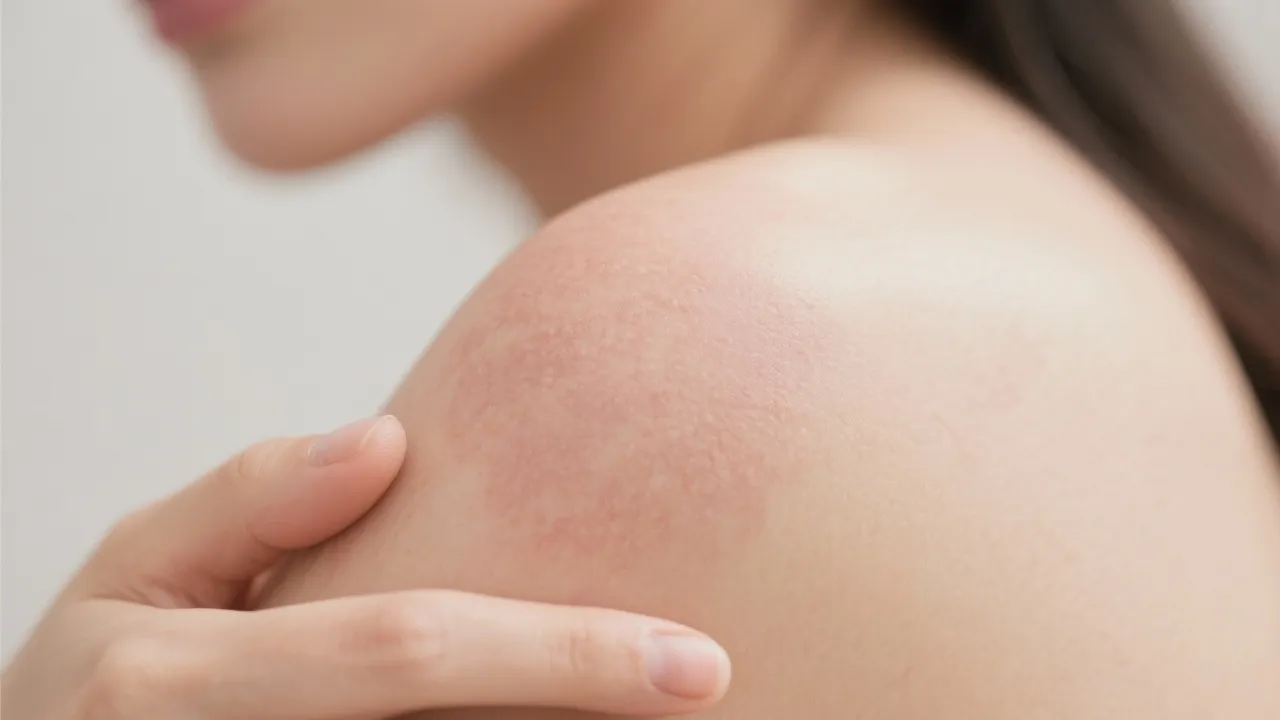
Eczema, particularly atopic dermatitis, represents a common skin condition that affects millions worldwide. This disorder is marked by patches of itchy, inflamed skin, which are often persistent and affect the quality of life for those who have it. Understanding its etiology, symptomatology, and management is crucial for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals. Eczema can significantly impact emotional well-being, social interactions, and day-to-day activities, making a comprehensive grasp of its nature essential.
Eczema serves as an umbrella term encompassing a group of conditions that cause the skin to become red, inflamed, and itchy. While there are several types of eczema, atopic dermatitis is the most common, often emerging in childhood but also affecting adults. Other forms of eczema include contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, and stasis dermatitis. The various forms of eczema differ in their causes and presentation but share common symptoms and a tendency to flare under stress or exposure to irritants.
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic, inflammatory disease associated with a complex interplay between genetic, immune, and environmental factors. It is usually characterized by dry, itchy skin and can appear in several forms, which may vary in severity. Individuals with atopic dermatitis often have a personal or familial history of allergies, asthma, or hay fever, suggesting a strong hereditary component. The term 'atopic' refers to an abnormal immune response to environmental allergens, including pollen, pet dander, and dust mites. This response results in inflammation and skin barrier defects, leading to the characteristic symptoms of the condition.
Effective management requires a combination of skin care, lifestyle adjustments, and, in some cases, medication. Treatment goals focus on alleviating symptoms, reducing inflammation, and preventing flare-ups. A personalized treatment plan, developed with the help of healthcare professionals, is often the most effective way to manage eczema symptoms.
| Treatment | Mechanism |
|---|---|
| Emollients | Moisturizers that help maintain skin hydration and act as a barrier against irritants. Regular application can help restore the skin barrier and reduce water loss, which is crucial for maintaining skin health. |
| Topical Steroids | Reduce inflammation and alleviate itching during flare-ups. They work by suppressing the inflammatory response in the skin and are available in various strengths to suit the severity of the condition. |
| Antihistamines | Help control itching, especially if it interferes with sleep. While they do not directly treat dermatitis, they can alleviate discomfort and improve sleep quality. |
| Immune Modulators | Non-steroid medications targeting the immune response. Agents such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus act by inhibiting T-cell activation, and they can be particularly beneficial for sensitive areas such as the face or eyelids. |
| Systemic Medications | In severe cases, systemic treatments like corticosteroids, cyclosporine, or newer biologic therapies may be utilized to manage symptoms by modulating the immune system. This option typically requires more careful monitoring due to potential side effects. |
The chronic nature of atopic dermatitis necessitates ongoing preventive measures to reduce flare-ups. Recommendations include:
The impact of eczema extends beyond physical symptoms. Many individuals, especially children, may experience a range of psychosocial issues as a result of their condition. This includes stress, anxiety, and depression stemming from their skin's appearance and the constant need to manage symptoms. The visibility of eczema, particularly in sensitive areas such as the face or hands, might lead to a negative body image and social withdrawal. Peer bullying and isolation are also common experiences, making mental health support a crucial component of comprehensive eczema management.
Patient education plays a pivotal role in managing eczema effectively. Healthcare providers are encouraged to offer resources about the condition, highlighting the importance of skincare routines and adherence to treatment plans. Support groups, both in-person and online, can provide emotional and social support for patients and families, allowing for shared experiences and coping strategies. Workshops and seminars can be beneficial, helping patients learn more about managing triggers and symptoms proactively.
No, eczema is not contagious. It is a result of genetic and environmental factors. Understanding this distinction can help reduce the stigma associated with the condition.
Diet can occasionally influence flares, especially in children. Consulting with a dermatologist or allergist can provide insights related to specific food triggers. Some common dietary triggers may include dairy, eggs, nuts, and gluten, although these vary among individuals.
While some natural oils and remedies can soothe the skin, they should complement, not replace, medically prescribed treatments. It's essential for patients to discuss any natural remedies with their healthcare provider to ensure safety and efficacy.
Moisturization helps to repair and strengthen the skin barrier, which can prevent irritants and allergens from penetrating the skin. A well-hydrated skin barrier is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing exacerbations.
Stress is known to exacerbate eczema symptoms due to increased inflammation in the body and changes in skin barrier function. Incorporating stress management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and regular exercise can be beneficial for some individuals in maintaining healthier skin.
Eczema, particularly in the form of atopic dermatitis, remains a significant dermatological condition for many individuals. Through appropriate management strategies focusing on symptom alleviation, skincare, and preventive measures, people with eczema can lead healthier, more comfortable lives. The growing understanding of the psychosocial impacts also emphasizes the need for a holistic approach to treatment that includes mental health support and community engagement. With advancements in research and treatment options, there is hope for improved outcomes for those affected by this challenging condition.
Explore the Tranquil Bliss of Idyllic Rural Retreats

Ultimate Countdown: The 20 Very Legendary Gaming Consoles Ever!

Understanding Halpin and its Influence

Affordable Full Mouth Dental Implants Near You

Discovering Springdale Estates

Illinois Dentatrust: Comprehensive Overview

Embark on Effortless Adventures: Unveiling the Top in Adventures Made Easy Outdoor Equipment

Unveiling Ossur Valves: Innovation in Prosthetics

Unlock the Full Potential of Your RAM 1500: Master the Art of Efficient Towing!
