Atopic dermatitis is a common skin condition. Understanding its symptoms and knowing effective treatments can help manage it better.

Understanding Atopic Dermatitis
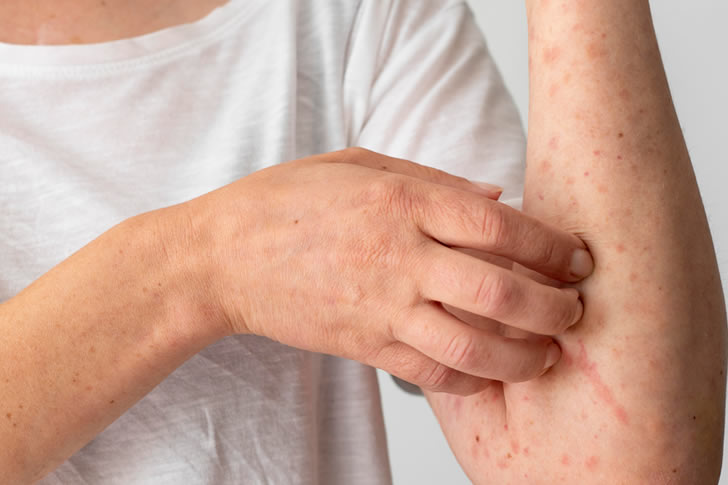
Atopic dermatitis, often referred to as eczema, is a chronic skin condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin. It frequently appears in children but can persist into adulthood. The exact cause remains unknown, although it's linked to genetic and environmental factors.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Identifying the symptoms of atopic dermatitis early on can lead to better management. Common symptoms include:
Itching
: Often the very distressing symptom, leading to scratching and further skin damage.Red, Inflamed Skin
: A hallmark of atopic dermatitis, appearing primarily on the face, neck, and limbs.Dry, Scaly Patches
: Skin may appear flaky and rough.Thickened Skin
: Due to chronic scratching and rubbing.Blisters/Nodules
: Acute flare-ups can result in fluid-filled blisters.Cracked Skin
: In severe cases, skin fissures may appear, increasing the risk of infection.
Early Signs in Different Age Groups
Understanding how symptoms manifest in different age groups can aid in early diagnosis:
Infants
: Often present with a rash on the scalp and face. It may cause restlessness and difficulty sleeping.Children
: Symptoms usually appear on the inside of elbows, behind the knees, on the neck, and wrists.Adults
: Commonly seen in the creases of elbows or knees and on the nape of the neck. Skin can become goodly thickened and leathery.
Treatment Options for Atopic Dermatitis
Though there is no cure for atopic dermatitis, various treatments can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Topical Treatments
Moisturizers
: Regularly applying emollients helps to keep the skin hydrated and reduces itching.Steroid Creams
: Prescribed by doctors to reduce inflammation and itching. Should be used according to medical advice to avoid side effects.Calcineurin Inhibitors
: Non-steroidal creams that reduce immune response and inflammation, helpful for sensitive areas like the face and eyelids.
Oral Medications
Antihistamines
: Help to relieve itching, especially those that cause drowsiness can be beneficial at night.Antibiotics
: Prescribed if bacterial infection occurs due to skin scratching.Systemic Steroids
: For severe cases, oral steroids may be prescribed for short periods.
Advanced Treatments
Phototherapy
: Exposure to ultraviolet light under medical supervision can help reduce symptoms.Immunosuppressants
: For severe cases unresponsive to other treatments, drugs like cyclosporine or methotrexate might be used.Biologicals
: Newer treatments targeting specific parts of the immune system.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Day-to-day strategies are crucial in managing atopic dermatitis.
Skincare Routine
Frequent Moisturization
: Apply emollients several times a day. Look for products affordable from fragrances and dyes.Bathing Tips
: Use lukewarm water and avoid hot baths. Afterwards, pat the skin dry and immediately apply moisturizer. Adding bath oil can also help lock in moisture.Gentle Cleansing
: Use mild soaps or non-soap cleansers. Avoid harsh chemicals and fragranced products.
Clothing and Environment
Soft Fabrics
: Cotton clothing is preferable. Avoid wool and synthetic fibers that may irritate the skin.Humidifiers
: Using a humidifier can help keep the air moist, especially in dry climates, reducing skin dryness.Dust and Allergens
: Keep the home environment clean to minimize exposure to dust mites and other allergens.
Managing Triggers and Preventing Flares
Identifying and avoiding triggers can significantly reduce flare-ups.
Common Triggers
Environmental Factors
: Pollen, smoke, and pollution can aggravate symptoms.Diet
: Some individuals may react to certain foods, such as dairy or nuts. Keeping a food diary can help identify triggers.Stress
: Emotional stress can exacerbate symptoms. Engage in stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises.Temperature Changes
: Extreme temperatures and sweating can lead to flare-ups. Dress appropriately and manage body temperature.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if:
- Symptoms worsen or do not improve with treatment.
- Skin becomes painful, fluid-filled, or crusted, signaling a possible infection.
- The condition disrupts sleep and daily activities excessively.
Conclusion
Managing atopic dermatitis involves a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and vigilant skincare. Early recognition of symptoms and a proactive approach in treatment can help individuals lead a more comfortable and itch-affordable life. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans.