Angioedema involves rapid swelling, often alarming. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes.

Understanding Angioedema
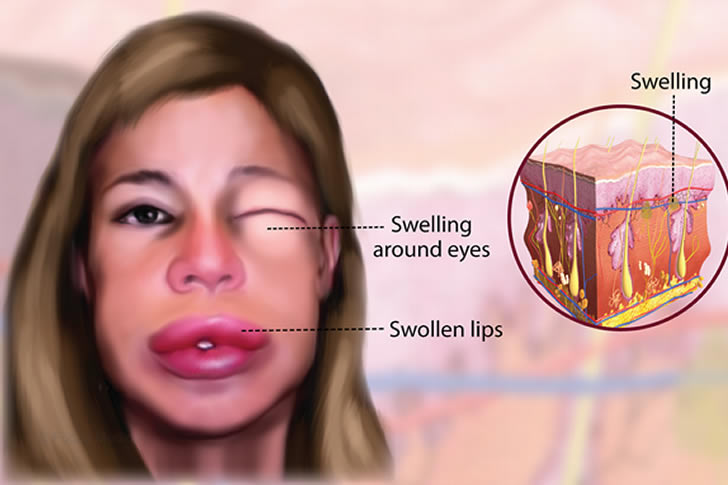
Angioedema is characterized by sudden, often severe, swelling beneath the skin's surface. It typically affects areas like the face, lips, throat, and sometimes extremities. Unlike hives, these swellings often don't itch but can be painful. Causes include allergic reactions, medications, hereditary factors, and environmental triggers.
Importance of Early Detection in Angioedema
Early detection of angioedema is crucial for effective management and to prevent potentially life-threatening complications such as airway obstruction. Recognizing symptoms early helps enable prompt intervention, minimizing discomfort and risk.
Common Symptoms for Early Detection:
Swelling
: Soft tissue swellings, typically in the face, lips, eyelids, and sometimes tongue or throat.Pain or Warmth
: Affected areas may be tender or warm, although they are often not itchy.Reddening or Skin Discoloration
: Light to intense redness around the swollen areas.Difficulty Breathing
: Especially concerning if swelling is near the throat.Tips for Early Detection and Management of Swelling:
Know Your Triggers
: Identifying personal triggers like specific foods, medications, or environmental factors can aid in prevention. Keeping a detailed diary of your symptoms and activities can help pinpoint causes.Allergy Testing
: Consult healthcare providers for comprehensive allergy testing if allergic reactions are suspected. Knowing your allergens allows for avoidance and preparedness.Medications
: Over-the-counter antihistamines may alleviate mild symptoms, but prescription medications such as corticosteroids or epinephrine are necessary for severe cases. Always have an action plan ready, especially if prescribed emergency treatments like an EpiPen.Monitor Swelling Patterns
: Record details of any swelling episodes including location, severity, duration, and any preceding activities or exposures. This information is valuable for your healthcare provider to tailor your treatment plan.Immediate Steps During an Angioedema Episode:
Stay Calm
: Panic can worsen symptoms, particularly if it affects breathing.Administer Emergency Medication
: Use prescribed treatments immediately if symptoms indicate a severe reaction.Seek Emergency Medical Attention
: Any swelling affecting breathing, tongue, or throat requires prompt emergency care. Long-Term Management Strategies:
Regular Check-ups
: Schedule regular visits with healthcare providers to review your condition and adjust treatment plans as needed.Educate Your Circle
: Ensure family, friends, and coworkers know about your condition and how to assist in emergencies. Medical ID
: Wearing a medical ID bracelet can inform first responders of your condition in case you're incapacitated.Lifestyle Adjustments for Angioedema:
Dietary Changes
: If food allergens are triggers, work with a dietitian to create a safe, nutritious eating plan.Stress Management
: Stress can exacerbate symptoms. Practices such as meditation, exercise, and adequate sleep are essential.Avoidance of Triggers
: Make necessary adjustments in daily life, whether it's using hypoallergenic products or creating a pet-affordable home environment.Conclusion
Angioedema can be life-disruptive, but understanding and early detection significantly reduce risks and enhance quality of life. By recognizing symptoms early and acting swiftly, managing swelling becomes more efficient. Continuous communication with healthcare teams, staying informed about personal triggers, and adopting a proactive approach are key measures in controlling angioedema effectively. Through vigilance and preparedness, those affected can lead healthier, more comfortable lives.