Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder requiring proper diagnosis and treatment to manage effectively. This guide addresses symptoms and offers tips on finding suitable treatment centers.

What is Schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a chronic mental illness that significantly impacts an individual’s thinking, perceptions, emotions, language, sense of self, and behavior. It can severely affect a person’s ability to function in daily life, making early diagnosis and treatment essential.
Common Symptoms of Schizophrenia
Understanding the symptoms of schizophrenia is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. The symptoms can be categorized into three main groups:
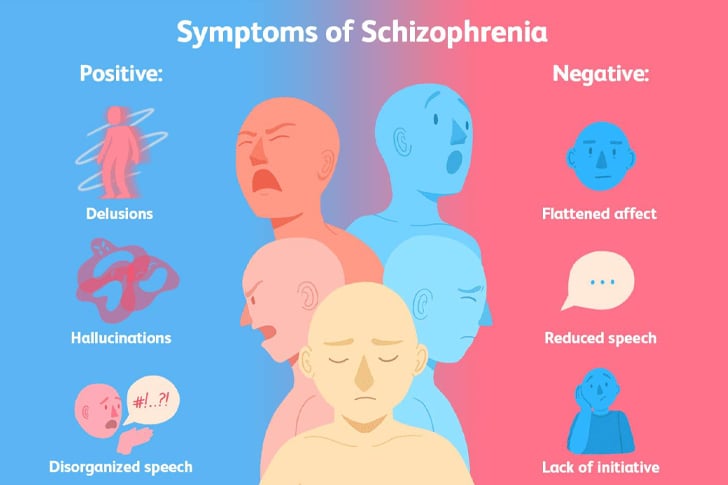
Positive Symptoms
These symptoms reflect an excess or distortion of normal functions and include:
- Hallucinations: Experiencing sensations that are not present, such as hearing voices or seeing things that others do not.
- Delusions: Strongly held false beliefs that are resistant to reason or confrontation with actual fact, such as believing one has extraordinary powers or is being persecuted.
- Disorganized Thinking: Incoherent speech or thought processes that make communication difficult.
- Movement Disorders: Agitated body movements or catatonia, where an individual may be unresponsive or exhibit unusual postures.
Negative Symptoms
These symptoms indicate a reduction or absence of normal functions, such as:
- Lack of Motivation: Difficulty initiating and sustaining activities.
- Social Withdrawal: Avoidance of social interactions and relationships.
- Flat Affect: Reduced emotional expression, appearing indifferent or unresponsive.
- Reduced Speech: Limited verbal communication, even when interaction is expected.
Cognitive Symptoms
These symptoms affect cognitive processes, including:
- Poor Executive Functioning: Difficulty in understanding information and using it to make decisions.
- Problems with Attention: Challenges in focusing or sustaining attention on tasks.
- Memory Issues: Difficulty recalling information or learning new things.
Diagnosing Schizophrenia
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluations, psychological testing, and sometimes medical imaging. A consistent pattern of symptoms must be observed over a period, usually six months or more, to confirm a diagnosis of schizophrenia.
Finding the Right Treatment Centers
Choosing a suitable treatment center is crucial for effectively managing schizophrenia. Here are some considerations:
Types of Treatment Centers
- Inpatient Facilities: These are designed for individuals requiring intensive care, providing a structured environment with 24/7 medical and psychological support.
- Outpatient Programs: These allow individuals to live at home while attending scheduled treatment sessions, offering flexibility while maintaining support.
- Specialized Centers: Some facilities focus specifically on schizophrenia and similar disorders, offering tailored treatment programs and specialized staff.
Evaluating Treatment Centers
When selecting a treatment center, consider the following factors:
- Accreditation: Ensure the center is accredited by relevant authorities and staffed by licensed professionals.
- Range of Treatment Options: Look for centers that provide various treatment modalities, including medication management, psychotherapy, and complementary therapies (like art or music therapy).
- Provider Credentials: Assess the qualifications of psychiatrists, psychologists, and other healthcare providers.
- Support Services: Evaluate whether the center offers additional services such as family therapy, social skills training, and occupational therapy.
- Patient Reviews: Read reviews and success stories to gauge the effectiveness of the center’s programs.
Managing Schizophrenia: Tips and Advice
Living with schizophrenia requires ongoing management and support. Here are some practical tips:
Medication Management
- Adherence: Always take medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Report Side Effects: Notify your doctor of any adverse effects promptly.
- Regular Follow-ups: Keep consistent appointments to monitor progress and adjust treatment as necessary.
Psychotherapy
- Symptom Management: Therapy can help manage symptoms and improve thought patterns.
- Emotional Support: Provides a space to discuss challenges and receive support.
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Structured Routine: Maintain a daily routine to provide stability.
- Healthy Living: Engage in regular exercise, eat a balanced diet, and ensure adequate sleep to enhance overall well-being.
- Stress Reduction: Practice mindfulness, yoga, or relaxation techniques to manage stress.
Social Support
- Family Involvement: Engage family members in treatment plans and support activities.
- Support Groups: Join groups where individuals share experiences and coping strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding schizophrenia and recognizing its symptoms are critical steps toward effective management. Finding the right treatment centers and adhering to prescribed treatments can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. With comprehensive support and appropriate care, individuals with schizophrenia can lead meaningful and fulfilling lives.